At about 10: 24 on July 10, 2021, in the water supply reconstruction project of Happiness Hospital in Five Blessingg Hall, Laishan Township, Wuchuan County in 2021, when two construction workers lowered the water pump in the tap water inspection well, a general production safety accident of anoxia and suffocation occurred, resulting in two deaths and a direct economic loss of 2,229,300 yuan.
In accordance with the Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) on Work Safety, Regulations on the Reporting, Investigation and Handling of Work Safety Accidents and other relevant national laws and regulations, on July 19th, the Office of the People’s Government of Hohhot issued the Notice of the Office of the People’s Government of Hohhot on the Establishment of an Investigation Team for the "July 10th" Water Pipeline Poisoning Accident in Wuchuan County, Inner Mongolia ([2021] 2-116)). The accident investigation team is headed by Yun Chunlei, secretary of the Party Committee and director of the Municipal Emergency Management Bureau, and Ren Rui, deputy secretary of the Municipal Commission for Discipline Inspection and deputy director of the Supervisory Committee, is the deputy head. The relevant responsible comrades and staff of the Municipal Public Security Bureau, the Municipal Water Affairs Bureau, the Municipal Federation of Trade Unions and the Wuchuan County People’s Government are composed together. The investigation team hired relevant experts to carry out accident investigation.
According to the principles of "four no-misses" and "scientific rigor, compliance with laws and regulations, seeking truth from facts and paying attention to practical results", the accident investigation team found out the process, causes, casualties and direct economic losses of the accident through on-site investigation, investigation and evidence collection, technical appraisal and simulation experiments, identified the nature and responsibility of the accident, put forward suggestions on handling the responsible persons and units, and put forward the accident reasons and outstanding problems exposed. The relevant situation is now reported as follows:
I. Overview of engineering projects and accident-related units
(A) the general situation of the project
In 2021, the water supply renovation project of Five Blessingg Hall Happiness Hospital in Laishan Township, Wuchuan County was built in 2016, involving 36 households with 72 people. When the project was completed, it shared a well with Dechangdian Village, built a new water tower, laid water distribution and household pipe network, and all houses were supplied with tap water, which has been running normally since the project was completed.
Since May 2021, Liu Qiongwen, deputy secretary of Laishan Township, Wuchuan County, and Wang Ermao, deputy director of Five Blessingg Tang Village Committee, have repeatedly called Fu Qiang, director of the County Water Affairs Bureau, and Zhang Junlin, head of the People’s and Livestock Drinking Office (hereinafter referred to as the "People’s Drinking Office") to report that the people in Happiness Hospital in Laishan Township have difficulty drinking water, and hope that the County Water Affairs Bureau can help solve the drinking problem of Happiness Hospital. After Zhang Junlin reported the situation to the County Water Affairs Bureau, the County Water Affairs Bureau regarded this project as a "practical project for the people On June 15th, 2021, a party meeting of the Bureau was held to study and decide to build a new deep well for the human drinking project of Five Blessingg Tangcun Mutual Aid Happiness Hospital in Laishan Township, and the human drinking office of the County Water Affairs Bureau was responsible for organizing the construction team.
In 2021, the water supply reconstruction project of Five Blessingg Hall Happiness Hospital in Laishan Township, Wuchuan County included a new water source well, a new well house, a new wellhead project, a 100-meter aqueduct, water pumps and other power facilities. The total investment of the project is 84,900 yuan.
(II) Construction unit: Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau.
In 2021, the water supply reconstruction project of Five Blessingg Hall Happiness Hospital in Haolaishan Township in Wuchuan County was studied by the party group of Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau, and the People’s Drinking Office of the County Water Affairs Bureau was responsible for the specific implementation. At the time of the incident, the People’s Drinking Office was an internal organization of the County Water Affairs Bureau and had no independent legal person qualification.
(III) Construction situation in the early stage of the project
On June 23, 2021, Zhang Jun Lin, head of the People’s Drinking Office of Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau, orally entrusted Zheng Yi (project construction leader, without construction qualification) to implement the water supply reconstruction project of Five Blessingg Hall Happiness Hospital in Laishan Township, Wuchuan County in 2021. Zheng Yi contacted Chen Jiarui, the legal representative of Wuchuan Chenyuan Well Industry Co., Ltd., who had been cooperating for a long time, to discuss well drilling, and then Wuchuan Chenyuan Well Industry Co., Ltd. dispatched a well drilling team to start well drilling on June 28 and July 3.
Second, the accident, emergency rescue and aftermath.
1. The accident happened.
On the basis of previous works, Zheng Yi and Li Wenhua (excavator drivers) excavated the trench along the water pipe on July 4th, and on July 5th, Zheng Yi hired two bridgehead workers to build inspection wells, and at the same time, Wang Linbiao and Zhang Erhong were employed to run the water pipe into the ditch. On July 6th, Wang Linbiao and Zhang Erhong were engaged in the pumping process (about 100 meters down), and Zheng Yi and the bridgehead workers continued to build inspection wells, and Wang Linbiao and Zhang Erhong finished pumping. At 8 o’clock on July 10th, Zheng Yi, the person in charge of on-site construction, led Li Wenhua (excavator driver), Wang Linbiao and Zhang Erhong to the construction site to continue their work. Zhang Erhong (who only wore safety helmet and did not take other protective measures) first went down the well to hang the wire rope and lift the pump. After the pump was lifted for about 10 meters, Zhang Erhong rose to the well, then sent electricity to pump water (the water was normal). After pumping for about 2 hours, he turned off the electricity and stopped the pump. Zheng Yi, the person in charge of on-site construction, found that the water was not clear enough, and decided to lower the water pump from about 90 meters in the well to about 110 meters (at this time, there were five people at the construction site, including Zheng Yi, Wang Linbiao, Zhang Erhong, excavator driver Li Wenhua and Wang Ermao, deputy director of Five Blessingg Hall Village Committee), and the construction worker Wang Linbiao (without taking any protective measures) went down to the well to prepare to lower the water pump. After Wang Linbiao went down to the bottom of the well, he immediately sat down against the well wall and the wellhead personnel shouted many times. At this point,Zhang Erhong mistakenly thought that Wang Linbiao had a heart attack and immediately went down to the well to rescue him (only wearing a helmet and taking no other protective measures). Zhang Erhong immediately squatted on Wang Linbiao’s body after going down the well. After Zheng Yi found the abnormality, he immediately prepared to go down to the well for rescue, which was discouraged by Li Wenhua. Later, Li Wenhua and Wang Ermao tied a rope to Zheng Yi’s body and tried to hang Zheng Yi with an excavator to enter the well for rescue. When Zheng Yi entered the wellhead about 1 meter, he suddenly felt unwell and immediately rose to the well, and the three people at the scene had to stop the rescue. After Zheng Yi rose to the well, he called the air compressor in turn, reported the situation to Zhang Junlin, and asked for rescue from 119 and 120. After the air compressor arrived at the scene, the air in the tap water inspection well was replaced. After the 119 and 120 people arrived at the scene, the 119 fire rescue officers and soldiers rescued Wang Linbiao and Zhang Erhong from the well. After being checked by 120 medical staff, they were declared dead.
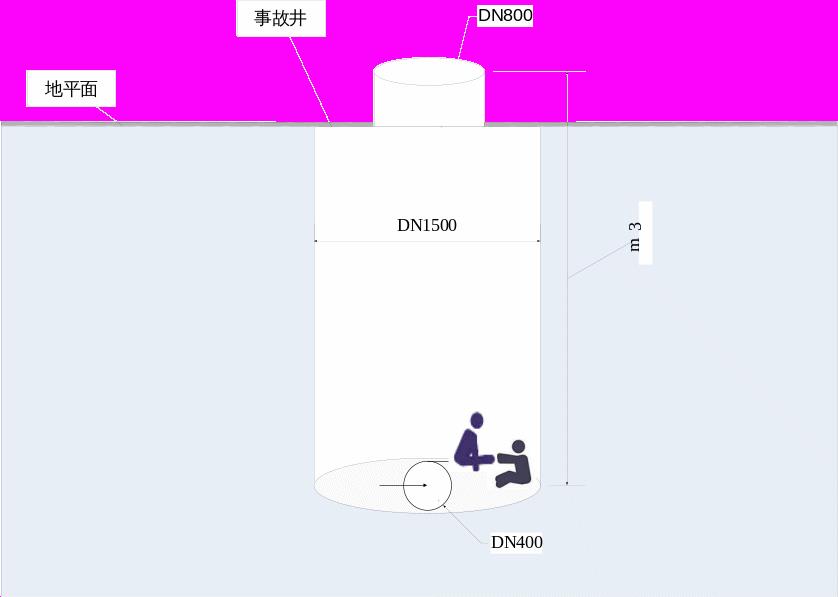
The accident well depth is 3m.
Wellhead diameter is 800 mm.
The accident well is 1500mm in diameter.
Well diameter is 400 mm.
Well depth is 132m m.






Schematic diagram of the incident site
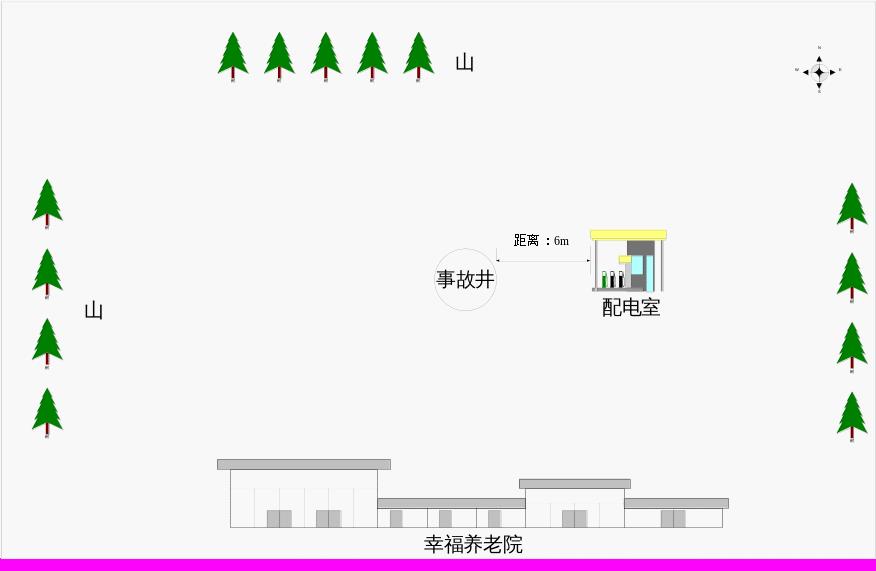
Schematic diagram around the incident site
matter Therefore, the weather conditions of the day occurred.
Therefore, the weather conditions of the day occurred.
2, the accident report.
After the accident, Zheng Yi, the person in charge of the on-site construction team, called 119 and 120 for rescue at 10: 25 and 10: 31 respectively. After receiving the alarm, the county fire rescue brigade informed the county emergency management bureau of the accident at 10: 35, and the main leaders and staff of the county emergency management bureau immediately rushed to the scene. After on-site verification, the county emergency management bureau reported the accident to the duty room of the municipal emergency management bureau and the duty room of the county people’s government at 12: 09 and 12: 10 respectively. Zheng Yi, the person in charge of the on-site construction team, telephoned Zhang Junlin, the person in charge of the People’s Drinking Office of the County Water Affairs Bureau, at 10: 20 on July 10th to report the accident at the construction site. After Zhang Junlin received the report, he telephoned Fu Qiang, the director of the County Water Affairs Bureau, and Fu Qiang and Zhang Jun Lin immediately set out at 11: 10 to participate in the disposal.
3, emergency rescue and on-site disposal
After the accident, Zheng Yi, the person in charge of on-site construction, called the air compressor in turn and asked 119 and 120 for rescue. After the air compressor arrived at the scene, it replaced the air in the tap water inspection well. At 10: 50, 119 fire rescue officers and soldiers arrived at the scene and carried out rescue. After on-site observation and understanding, two construction workers were in a coma in the tap water inspection well with a depth of three meters. There was an air supply pipeline with a steel cable and a water pipe in the well, and the air compressor had been supplying air to the well for more than 20 minutes. The scene was in an emergency, and the fire rescue commander immediately gave the order to carry out the rescue. The fire rescuers made safety protection, wore air respirator and wore safety ropes. With the assistance of other fire rescuers, they slowly entered the inspection well, and rescued two comatose people by using safety ropes in turn, and then handed them over to the ambulance personnel of the 120 emergency center at the scene for emergency treatment. After examination by medical staff, they were confirmed to have no vital signs and declared dead.
4, the aftermath.
On July 10th, Wuchuan County People’s Government took the initiative to intervene to appease family members and properly handle compensation matters. The leaders of Wuchuan County cooperated with the people’s government of Laishan Township and the heads of emergency and water affairs departments to express their condolences to the families of the deceased, expressed the concern and condolences of the county party committee and government, and held consultations on compensation. At present, compensation for the aftermath has been completed.
Three, the accident caused casualties and direct economic losses.
Two people were killed in the accident. The direct economic loss was RMB 2,229,300.
Four, the cause analysis and nature of the accident
(A) the direct cause
1. On the basis of the previous project, at 10 o’clock on July 10th, the oxygen content in the inspection well was about 1.0% due to the continuous pumping of water by the on-site pump for about 2 hours (relevant conclusions were drawn from three on-site gas detection tests after the incident by a third-party testing organization). At this time, two construction workers, Wang Linbiao and Zhang Erhong, rushed into the well to lower the water pump without wearing the necessary labor protection articles for working in a limited space, which eventually led to the death of two construction workers due to hypoxia and suffocation.
lack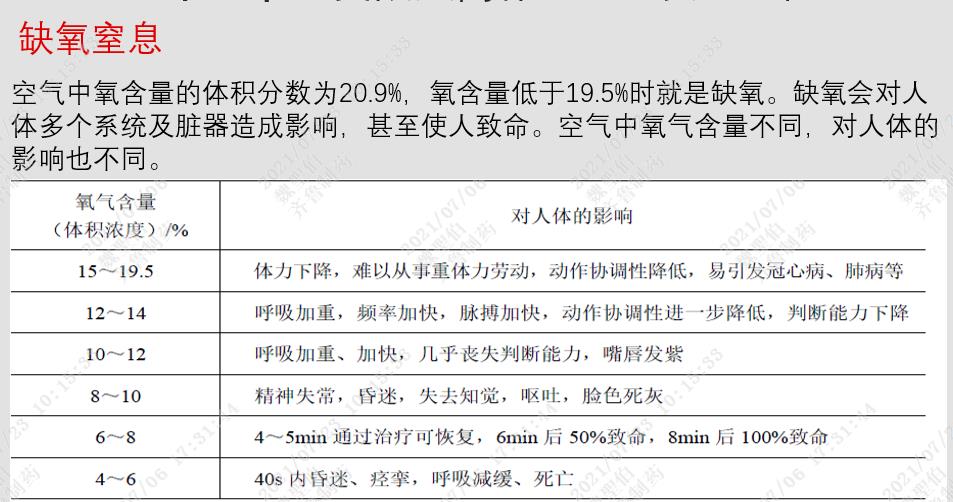 ??
??
Effect table of oxygen asphyxia
2. The construction site was not equipped with emergency rescue equipment and equipment that met the requirements. After the first construction worker went into a coma in the well, the second construction worker rushed into the well to rescue without wearing labor protection articles and emergency rescue equipment and equipment that met the requirements, resulting in an increase in the death toll.
(2) Indirect causes
1. The Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau contracted the water supply renovation project of Five Blessingg Hall Happiness Hospital in Laishan Township in Wuchuan County in 2021 to Zheng Yi, an individual who did not have the conditions for safe production and the corresponding qualifications, and as the competent department of the industry, he failed to perform the duties of safety production supervision, neglected the management of the construction process and failed to implement the duties of safety production supervision.
2. The on-site construction team organized by Zheng Yi, without business license and construction qualification, illegally contracted the water supply renovation project of Happiness House in Five Blessingg Hall, Laishan Township, Wuchuan County in 2021, and did not organize the construction in accordance with the relevant regulations on limited space operations during the construction process, which belongs to illegal contracting and illegal organization of construction operations.
3. Zheng Yi, the person in charge of the on-site construction team, failed to make safety technical disclosure to the employees before the operation and failed to formulate emergency measures, which led to the employees’ blind operation and blind rescue, which eventually led to accidents and an increase in the number of deaths.
4. The construction site lacks the necessary testing facilities for limited space operation. Before entering the limited space operation, the construction personnel failed to perform the examination and approval procedures according to the regulations on limited space operation management, and did not test the oxygen content and toxic and harmful gases in the operation well.
(3) Identification of the nature of the accident
After investigation, it was found that the "July 10" suffocation accident of Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau was a general production safety liability accident that violated the management of limited space operations.
Five, suggestions on the handling of the accident related responsible units and personnel.
(1) Persons who suggested to be exempted from accountability (2 persons)
1. Wang Linbiao, male, 62 years old, a construction worker, with weak safety awareness, rushed into the well to work without wearing the necessary labor protection articles for entering a limited space, which led to the accident. He was directly responsible for this accident, but in view of his death in the accident, it is suggested that he be exempted from being investigated for responsibility.
2. Zhang Erhong, male, 58 years old, is a construction worker with weak safety awareness. He rushed into the well to work and carry out rescue without wearing the necessary labor protection articles for entering a limited space, resulting in an increase in the number of casualties. He was directly responsible for this accident, but in view of his death in the accident, it is suggested that he be exempted from being investigated for responsibility.
(2) Persons who suggest to be investigated for criminal responsibility (1 person)
1. Zheng Yi, male, 58 years old, is the head of the on-site construction team. He has no business license and construction qualification. He illegally contracted the water supply renovation project of Happiness Hospital in Five Blessingg Hall, Laishan Township, Wuchuan County in 2021, and did not organize the construction in accordance with the relevant regulations on limited space operation during the construction process, which belongs to illegal contracting and illegal organization of construction operations. Before the operation, he did not make safety technical disclosure to employees and did not formulate emergency measures, resulting in blind operation and blind rescue of employees. In the end, it led to an accident and an increase in the number of deaths. He was mainly responsible for this accident and was suspected of constituting the crime of major liability accident. It is suggested that the judicial organs should investigate his criminal responsibility.
(3) persons who are recommended to be given disciplinary sanctions (3 persons)
1. Zhang Junlin, male, 45 years old, party member, head of the People’s Drinking Office of Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau, verbally entrusted the water supply renovation project of Five Blessingg Hall Happiness Hospital in Laishan Township, Wuchuan County in 2021 to Zheng Yi, an individual who did not have the construction qualification, and neglected the supervision during the implementation of the project, and was mainly responsible for this accident. It is suggested that the discipline inspection and supervision department give him disciplinary sanctions.
2. Tian Wenxiong, male, 58 years old, party member, member and deputy director of the Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau, attended the meeting of the bureau’s party group and agreed to organize the construction team to carry out the water supply renovation project of Five Blessingg Hall Happiness Hospital in Laishan Township, Wuchuan County in 2021. As the leader in charge of the bureau, he neglected the supervision of the construction project and the construction qualification of the construction team, and was responsible for the leadership in this accident. It is suggested that the discipline inspection and supervision department give him disciplinary sanctions.
3. Fu Qiang, male, 58 years old, party member, Party Secretary and Director of Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau, attended the party group meeting of Wuchuan County and agreed to organize the construction team to carry out the water supply renovation project of Five Blessingg Hall Happiness Hospital in Laishan Township in Wuchuan County in 2021. As the main leader of the bureau, he neglected the supervision of the construction project and the construction qualification of the construction team, and took the leadership responsibility in this accident; And after receiving a phone call from Zhang Junlin to report the accident, Fu Qiang and Zhang Junlin rushed to the scene to participate in the disposal at the first time, resulting in their failure to report the accident to the county people’s government within the specified time, which was due to negligence and there was no subjective intention. It is suggested that the discipline inspection and supervision department give them disciplinary sanctions.
(4) Suggestions on the treatment of Wuchuan County People’s Government and Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau.
1. It is suggested that Wuchuan County People’s Government carry out county-wide informed criticism on Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau.
2. It is suggested that Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau be instructed to make a written inspection to Wuchuan County People’s Government.
3. It is suggested that the Hohhot Municipal People’s Government conduct a informed criticism for Wuchuan County People’s Government.
4. It is suggested that Wuchuan County People’s Government should be instructed to make a written inspection to Hohhot Safety Production Committee.
VI. Preventive Measures and Suggestions
In order to conscientiously sum up the lessons of the accident and prevent the recurrence of similar accidents, the following preventive and corrective measures are put forward:
1. Strengthen the safety management of construction projects, and compact the safety production responsibility of the participating enterprises. Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau must carry out the work of safety in production in strict accordance with the provisions of the Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) on Safety in Production, that is, "safety must be managed in the industry, safety must be managed in the business and safety must be managed in the production and operation", and immediately carry out the work of "large-scale investigation and rectification" of production safety accidents of all construction projects participating units in the industry, establish "one enterprise and one file", and require all units to strictly implement the main responsibility of safety in production, strengthen safety management and strengthen risk awareness. Establish a ledger for the investigation and management of hidden dangers, establish and improve the safety production responsibility system and safety production rules and regulations for all employees, increase the investment guarantee for safety production funds, materials, technology and personnel, improve the level of safety production and ensure safety production.
2. Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau should further standardize the contract management of contractors. Units undertaking design, construction, supervision, installation and debugging must have corresponding qualifications. It is strictly forbidden to contract out production and operation projects, sites and equipment to units and individuals that do not have the conditions for safe production or corresponding qualifications, and resolutely put an end to the behavior of contracting projects without qualifications, linking or borrowing qualifications. Moreover, all parties involved in the construction should further standardize and perform the contract signing of construction projects and employees, and the contract must include relevant provisions on safety production management or sign a special safety management agreement.
3, strengthen safety education and training, strengthen the safety awareness of employees. Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau and all construction project contractors in the industry should immediately conduct safety training and education for employees through various forms and channels, establish and implement a safety training and education system, improve employees’ awareness and skills of accident prevention and disposal, and standardize employees’ safety production behavior.
4. Standardize the management of dangerous operations. Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau and all construction project contractors in the industry must formulate perfect safety production rules and regulations and operating procedures, strictly perform the examination and approval procedures for dangerous operations, arrange special personnel to supervise, inspect, guide and coordinate the whole process of the construction site, and equip the job site with necessary emergency rescue equipment, equipment and materials when carrying out hoisting, hot work, temporary electricity use, limited space and other dangerous operations specified by the emergency management department of the State Council in conjunction with relevant departments of the State Council in the future. The main person in charge, safety management personnel and special operations personnel shall hold relevant certificates.
5. Effectively improve the emergency response capability of enterprises. Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau should urge all enterprises in the industry to strengthen daily emergency training, improve the knowledge of accident prevention, hedging, escape, self-help and mutual rescue of employees, regularly carry out daily emergency rescue drills, improve the emergency handling skills of employees, and ensure that once an abnormal situation occurs, employees can effectively deal with it at the first time, so as to avoid the expansion of the situation or the occurrence of secondary accidents and minimize losses.
6, the implementation of comprehensive supervision responsibility for production safety. Wuchuan County Emergency Management Bureau should earnestly draw lessons from accidents, find weak links and regulatory loopholes, strengthen law and order, adhere to the "red line" of safety production, severely crack down on all kinds of illegal and illegal acts, and protect the health and life safety of the broad masses of people. It is necessary to improve the ability to perform their duties, guide various industries to strengthen safety management, and prevent production safety accidents.
7. All regions and relevant departments should "draw inferences from others", carry out in-depth publicity on the newly revised People’s Republic of China (PRC) Law on Work Safety and the Interim Provisions on Safety Management and Supervision of Limited Space Operation in Industry and Trade Industry (formerly Order No.59 of the State Administration of Work Safety) and other laws and regulations, and carry out special actions of "large-scale investigation and rectification" of hidden dangers in production in various industries and fields, so that enterprises and employees can know the law.
Wuchuan County Water Affairs Bureau suffocated on July 10th.
General production safety accident investigation team
















 Therefore, the weather conditions of the day occurred.
Therefore, the weather conditions of the day occurred. ??
??